2025 Home oxygen therapy, are you doing it right?
Oxygen therapy (i.e. oxygen inhalation therapy) is a commonly used clinical treatment method. From home to hospital, from infants to the elderly, and even hospice care, its wide range of applications involves all clinical disciplines.
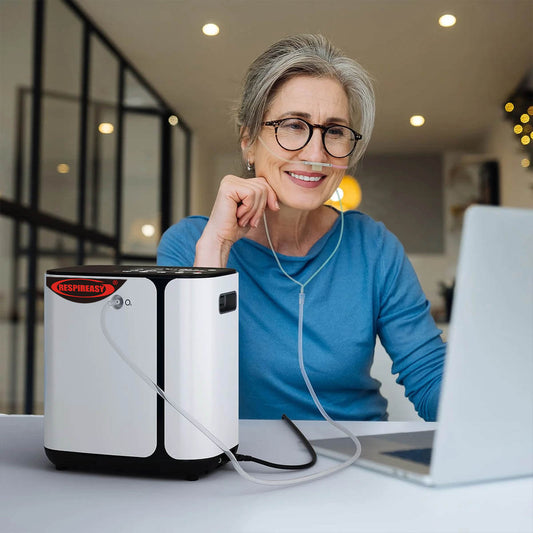
Home oxygen therapy refers to the treatment method in which patients return home to continue long-term oxygen inhalation after their condition stabilizes. It is an important measure to correct hypoxia and improve the quality of life. Studies have shown that long-term home oxygen therapy can improve the survival rate and reduce the hospitalization rate for patients with poor lung function.
Which groups need home oxygen therapy?
1. Patients with chronic hypoxemia, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (without carbon dioxide retention), pulmonary interstitial fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension, severe heart failure, sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome and other lung diseases, as well as heart failure patients, blood oxygen saturation is less than 94%, hypoxemia exists in the resting state, arterial oxygen partial pressure <55mmHg or arterial oxygen saturation <88%, all of which are recommended for oxygen therapy.
2. Some patients have a mild hypoxia (hypoxemia) state or do not persist. Hypoxia is often induced or aggravated by increased activity, excessive mental tension, overeating, and supine sleep at night. Regular, intermittent short-term oxygen inhalation or intermittent emergency oxygen inhalation can be used for treatment, such as: adult congenital heart disease, coronary heart disease, patients with a history of cerebral infarction, excessive obesity, lung cancer, etc.
3. Some patients in the recovery period of acute diseases, such as acute myocardial infarction, acute cerebral infarction, severe myocarditis, severe pneumonia, or after cardiothoracic surgery, may have staged mild hypoxia or be prone to hypoxemia. Intermittent oxygen therapy can also be used to improve hypoxia, improve heart, lung, and brain function, and promote recovery.
4. After an acute bronchial asthma attack or an epileptic seizure, patients will have varying degrees of hypoxia. At this time, emergency oxygen therapy (10-20 minutes) can not only improve dyspnea and reduce brain damage, but also reduce the recurrence of acute attacks caused by hypoxia.
What are the devices for home oxygen therapy?
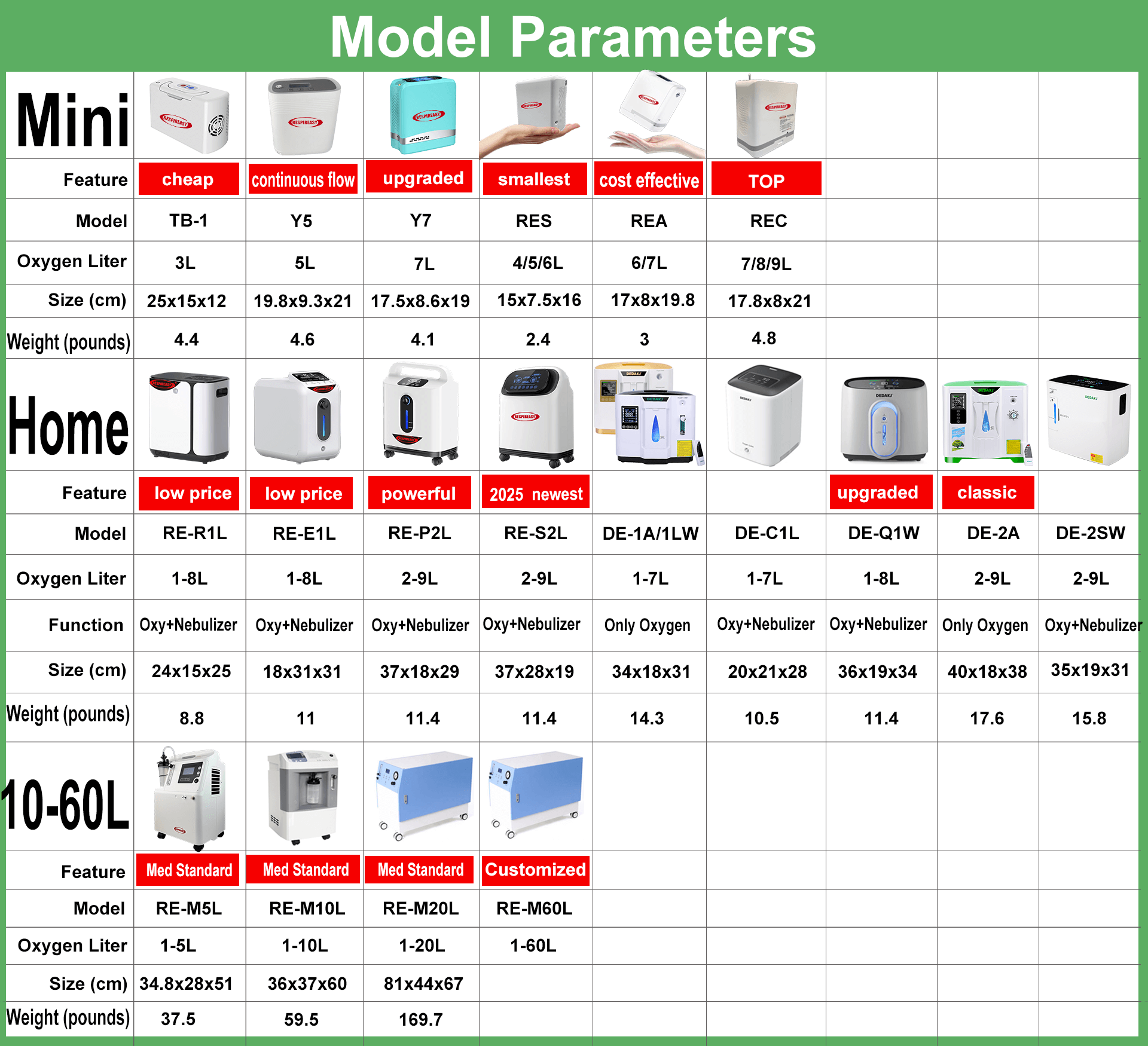
Common sources of oxygen for home oxygen therapy are medical oxygen cylinders, oxygen concentrators, and liquid oxygen, which are divided into fixed and portable types depending on whether they can be carried with you.
1. Medical oxygen cylinder: stores compressed medical oxygen, with a pressure valve and flow meter connected to the cylinder to observe the remaining gas volume and adjust the oxygen flow rate. 10-liter oxygen cylinders are most commonly used for home oxygen therapy, while 1-liter and 4-liter oxygen cylinders are often carried with you.
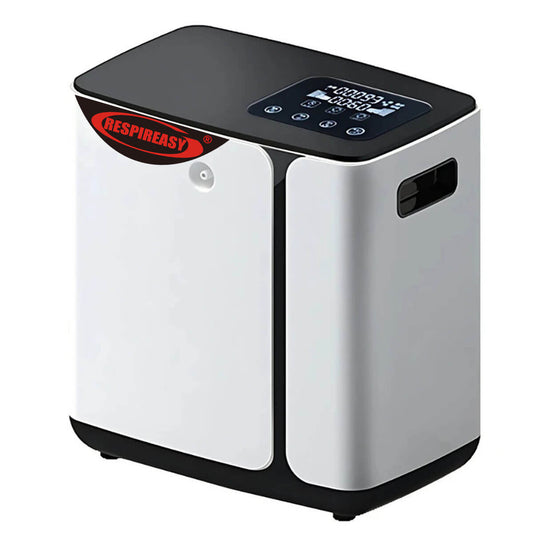
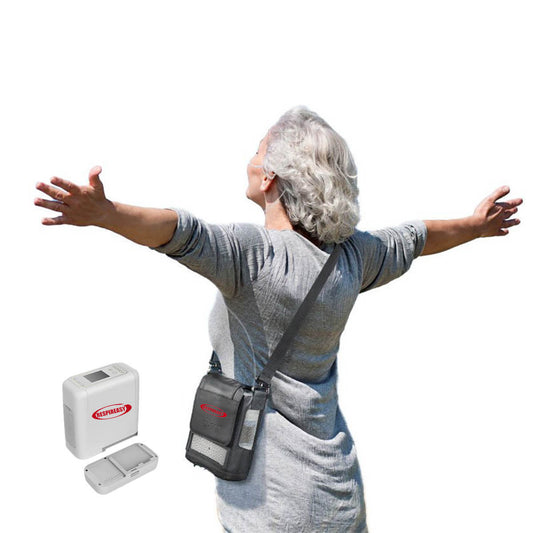
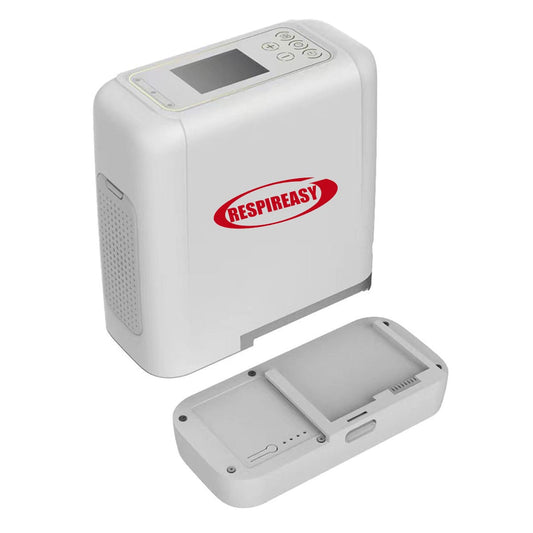
2. Oxygen concentrator: Most of them are oxygen concentrators, and the output of the oxygen concentrator is usually measured in "liters/minute". Low-flow oxygen concentrators can deliver an oxygen flow rate of 0.5-5 liters/minute; high-flow oxygen concentrators can deliver an oxygen flow rate of 10-15 liters/minute. Oxygen concentrators can also be divided into fixed and portable types, and portable oxygen concentrators are powered by built-in rechargeable batteries.
DEDAKJ Continuous Oxygen Generator 1-8L Adjustable Oxygen Concentrator Machine DE-Q1W for Home Use with Nebulizer Function, Low Noise Whole Night Working
DEDAKJ 1-7 Liter Home Oxygen Concentrator Continuous Flow Oxygen Generator Portable Oxygen Making Machine 110V/220V DE-1LW
1.1kg Lightweight Portable Travel Oxygen Concentrator O2 Generator 1-6 Liter with Backpack Battery Powered Home Mini O2 Oxygene Concentrator Machine Price

👍👍👍2025 Small Lightweight Oxygen Concentrator 7 Liter 93% Purity Mini Portable O2 Generator Oxygem Machine Low Noise with Lithium Battery
3. Liquid oxygen: Liquid oxygen supply is to convert stored liquid oxygen into gaseous oxygen after pressurization and vaporization. Liquid oxygen tanks are easy to carry and suitable for outdoor oxygen supply. It is suitable for young people and patients with hypoxemia who spend more than 3 hours outdoors every day.
Oxygen delivery device
1. Nasal cannula: Nasal cannula is the most commonly used oxygen delivery device, one end of which is connected to an oxygen concentrator or oxygen cylinder. This method is simple and easy to use. Nasal cannula is generally suitable for low-flow oxygen inhalation (except for high-flow nasal oxygen therapy machines).
2. Mask: Mask-type cannula is suitable for patients with severe conditions, significantly decreased oxygen saturation and no hypercapnia. When using, cover the mask on the mouth and nose and fix it with an elastic band. Note that for patients with combined carbon dioxide retention, long-term wearing of oxygen masks may increase the risk of repeated inhalation of carbon dioxide.
Concentration and time of home oxygen therapy
Low-concentration oxygen (inhaled oxygen concentration <40%): used for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease accompanied by carbon dioxide retention, which can avoid suppressing the respiratory center and aggravating hypercapnia.
Medium-concentration oxygen inhalation (oxygen concentration 40%-60%) and high-concentration oxygen inhalation (oxygen concentration>60%): Suitable for patients with simple hypoxemia without obvious carbon dioxide retention, i.e. type I respiratory failure.
For patients with hypoxemia who need long-term oxygen therapy, as well as patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cor pulmonale, the oxygen flow rate is generally set to 1-2 liters/minute, for more than 15 hours a day, and oxygen is inhaled as long as possible, i.e. low-concentration continuous inhalation. However, if the patient's shortness of breath is significantly aggravated after activity and the oxygen partial pressure decreases, a short-term high-concentration oxygen supply can be given, and the oxygen flow rate can be reduced after the symptoms are relieved. The high-concentration oxygen inhalation time cannot be too long. When the oxygen concentration is >60% and lasts for more than 24 hours, oxygen poisoning may occur.
What is the role of home oxygen therapy?
1. Improve hypoxemia and meet the needs of tissue metabolism;
2. Relieve pulmonary hypertension caused by hypoxia and delay the occurrence and development of cor pulmonale;
3. Relieve bronchospasm, reduce dyspnea, and improve ventilation dysfunction;
4. Improve sleep, improve exercise endurance and quality of life, and prolong life.
What should be paid attention to in home oxygen therapy?
1. Home oxygen therapy should be persisted for a long time, and oxygen should not be inhaled until the acute onset.
2. The effect of oxygen therapy should be closely observed during oxygen inhalation. If the discomfort symptoms such as palpitations and dyspnea are relieved, it means that oxygen therapy is effective; if the effect is not good, seek medical help to find the cause.
3. At the same time, attention should be paid to the warming and humidification of the respiratory tract during oxygen therapy. The inhaled oxygen should pass through the humidification bottle and the necessary heating device to prevent the dry and cold gas from irritating the respiratory mucosa, inducing coughing, or causing sputum to dry and form sputum crusts, which are not easy to cough out.
4. Regularly replace the humidifying liquid in the humidification bottle, clean the tip of the nasal cannula, and regularly replace the oxygen generator filter.
5. Safe use of oxygen: Keep away from open flames and avoid contact with fire sources in places with oxygen supply equipment. Do not smoke and avoid operations that generate static electricity or electric sparks.