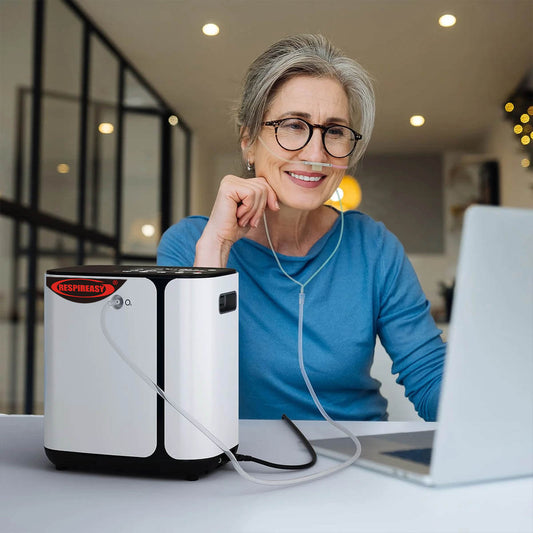
Home oxygen concentrator precautions
Oxygen inhalation can relieve fatigue and reduce stress, but if you do not follow the doctor's advice and blindly inhale oxygen without limit, high-concentration "oxygen therapy" may cause complications, which will inhibit breathing, cause oxygen poisoning, discomfort and pain behind the sternum, aggravate when inhaling, cough, dyspnea, etc., which is not good.
In addition, for the human body, oxygen cannot be stored, and the human hemoglobin's oxygen-carrying capacity is also limited. Therefore, oxygen inhalation cannot increase arterial blood oxygen and improve the brain's oxygen output. Oxygen can only act as a placebo. There is no reliable evidence to prove that oxygen inhalation has a very obvious health-care effect. It should be emphasized that oxygen inhalation cannot improve intelligence. It is only a "fuel aid" in the oxidative metabolism of the nutrient sugar. The brain is the organ with the highest oxygen consumption in the body. During intensive mental work, the amount of brain oxygen will increase, but it is very limited. It can be satisfied by increasing blood through self-regulation.
Oxygen inhalation also requires some precautions, such as the following points: ☟☟
1. The oxygen flow rate for health care purposes should not be greater than 3 liters/minute, and the total use time per day should not exceed 1 hour. High-concentration oxygen supply should not be used for too long. It is generally believed that if the oxygen concentration is >60% and lasts for more than 24 hours, oxygen poisoning may occur. In acute respiratory failure such as respiratory failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome, acute poisoning (such as carbon monoxide poisoning, i.e., gas poisoning), respiratory depression, etc., high-concentration or pure oxygen must be used for rescue every second, but it should not be used for a long time to prevent oxygen poisoning or other complications. Under normal circumstances, our lungs maintain a balance with the external atmospheric pressure by filling with nitrogen that is difficult to be absorbed by the lungs under normal pressure. When inhaling high-oxygen air, the nitrogen content in the alveoli gradually decreases, and oxygen may be absorbed by the alveoli, resulting in a decrease in the internal alveolar pressure and causing atelectasis.
2. Giving high-concentration oxygen to patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease may cause respiratory depression and worsen the condition. Generally, controlled (i.e., low-concentration continuous) oxygen should be given. When chronic respiratory failure loses compensation, oxygen inhalation must take into account the increase in blood oxygen partial pressure. Too high blood oxygen partial pressure can weaken the reflex stimulation of the carotid sinus to the respiratory center, thereby reducing ventilation and aggravating carbon dioxide retention. So use oxygen with caution.
3. Prevent contamination and catheter blockage. Nasal congestion, oxygen delivery catheter, humidification and heating device, ventilator pipeline system, etc. should be replaced and cleaned and disinfected regularly to prevent cross infection. Oxygen inhalation catheters and nasal congestion should be checked at any time for secretion blockage and replaced in time. To ensure effective and safe oxygen therapy.
4. Pay attention to heating and humidification during oxygen therapy. Maintaining a temperature of 37°C and a humidity of 95% to 100% in the respiratory tract is a necessary condition for the normal clearance function of the mucociliary system in the trachea. Therefore, oxygen inhalation should be done through a humidifier bottle and necessary heating devices to prevent the inhalation of dry and cold oxygen from stimulating and damaging the airway mucosa, causing sputum dryness and affecting the "scavenger" function of the cilia.
In short, when inhaling oxygen, it should be noted that improper use of oxygen also has side effects, especially for patients. It should be used under the guidance of a physician. Under normal circumstances, healthy people generally do not suffer from hypoxia, and the oxygen delivered to human tissues always exceeds the oxygen consumption of tissues. The atmosphere contains about 20% oxygen, which is a relatively constant value. Air pollution only increases some impurity particles and does not affect the concentration of oxygen in the air. Even in densely populated areas, it is sufficient to supply people's needs.