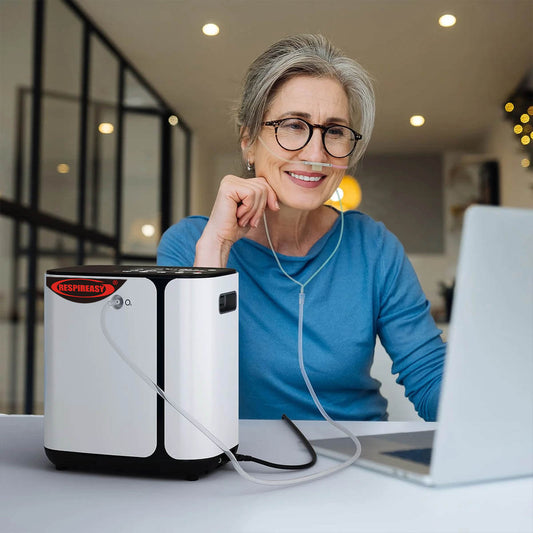
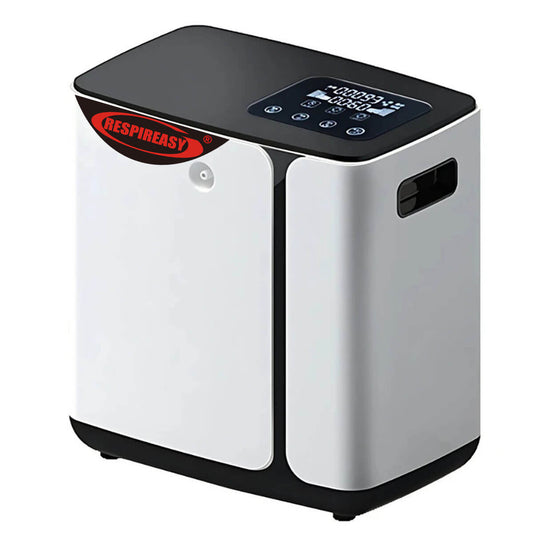
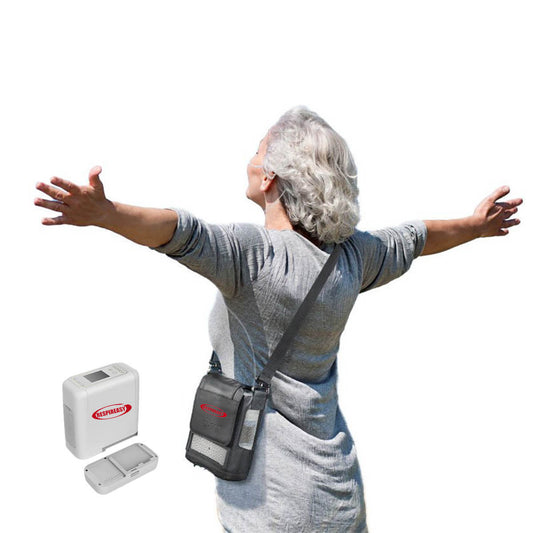
Oxygen inhalation is one of the most direct and effective treatment measures to improve hypoxic diseases. Long-term home oxygen therapy can correct hypoxemia, reduce the damage of hypoxia to important organs such as the heart, brain, kidneys, and lungs, and improve the quality of life of patients. The key to home oxygen therapy is scientific oxygen use guidance and medical-grade oxygen concentrators. As a basic and widely used equipment, oxygen concentrators are a hot topic that clinical engineers are often consulted about.
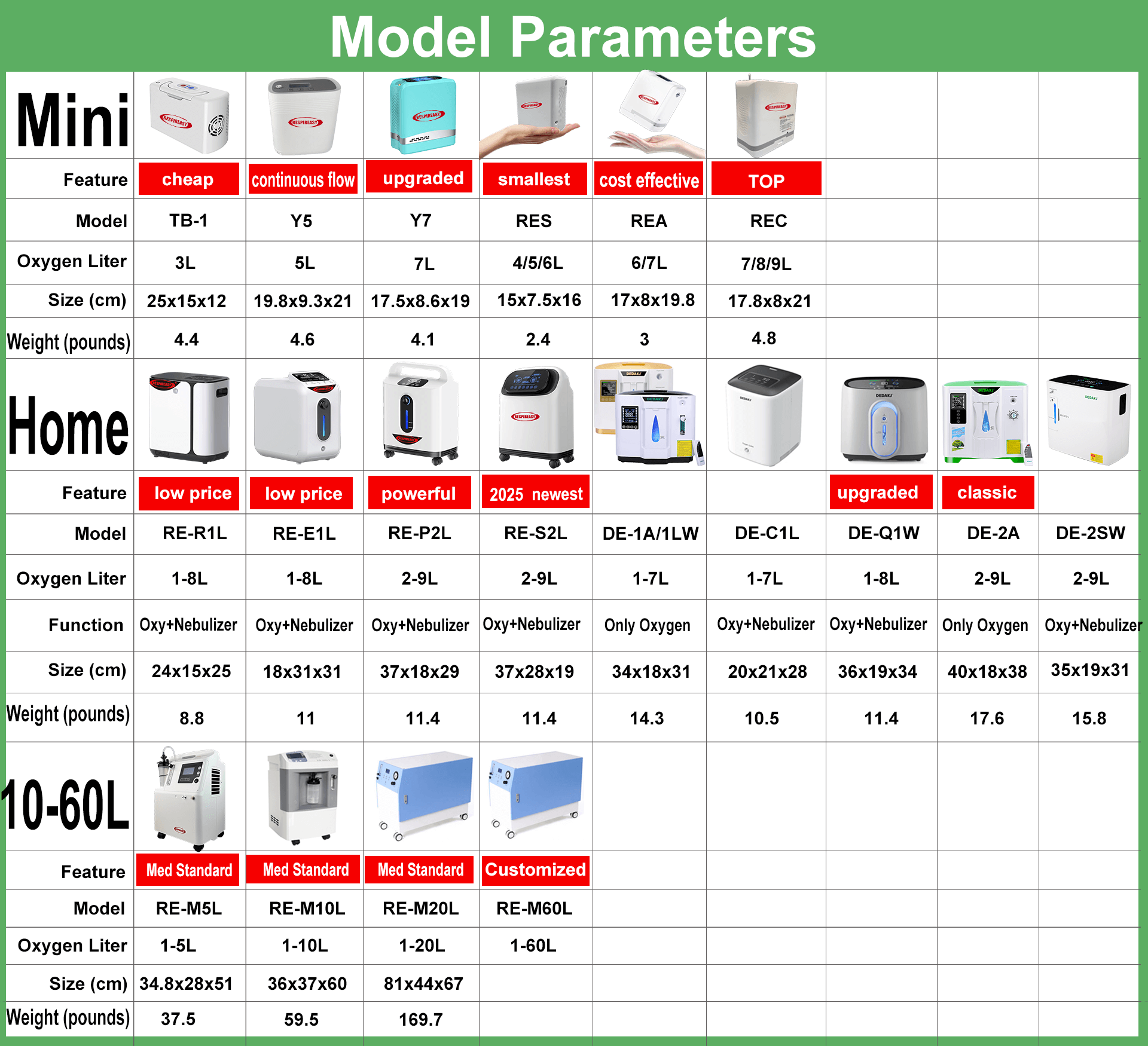
Home oxygen concentrator equipment purchase guide
Definition of oxygen concentrator specifications (liters)
X-liter oxygen concentrator means that the oxygen concentration is still maintained at 93%±3% at the maximum output of X liters. If X≥3, it can be used for medical purposes and is called a medical oxygen concentrator (with a medical device registration certificate), otherwise it is a health care oxygen concentrator. The maximum liters of oxygen concentrators are backward compatible.
Oxygen concentrators of various specifications are suitable for the following groups
1L oxygen concentrators are often used for health care, and are suitable for pregnant women, students, office workers and other people who use their brains for a long time, to achieve health care effects such as enhancing immunity;
3L oxygen concentrators are often used for elderly health care, hypertension, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular hypoxia, hyperglycemia, obesity, etc.;
5L oxygen concentrators are often used for cardiopulmonary functional diseases (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cor pulmonale);
8L oxygen concentrators are often used for special patients with high oxygen flow and long-term oxygen inhalation.
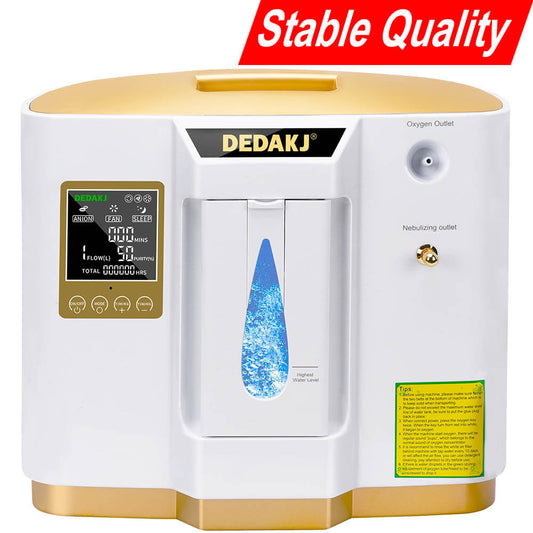
Working principle of oxygen concentrator
Using air separation technology, the air is first compressed at a high density, and then the molecular sizes of the components in the air are used to separate them under molecular sieve adsorption. It is separated into oxygen and nitrogen, and then the nitrogen in the air is separated from the oxygen, and finally a high concentration of oxygen is obtained.
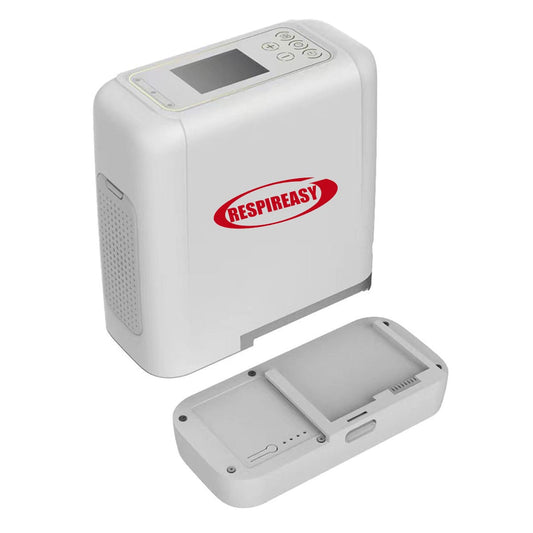
Compressors and molecular sieves are the core components of oxygen concentrators. The larger the power of the compressor and the finer the molecular sieve, the basis for improving the oxygen production capacity, which is roughly reflected in the volume, component material and process technology of the oxygen concentrator.
Supporting oxygen inhalation tools
Nasal cannula oxygen inhalation is divided into unilateral and bilateral nasal cannula and nasal plug method. If you use nasal plug or nasal cannula to inhale oxygen, you should close your mouth to breathe. Generally, bilateral nasal cannula oxygen inhalation is selected. Long-term unilateral nasal cannula has greater irritation to the nasopharynx; nasal plug placed in the anterior nostril is more comfortable for oxygen inhalation, light but easy to fall off. Mask oxygen inhalation affects speaking and eating, and compresses the face, so it can only be used for a short period of time.
Matching oxygen equipment
Oxygen concentrators can solve the problem of inhaled oxygen concentration, but cannot solve the problem of inhalation. When respiratory distress or sleep apnea syndrome occurs due to reasons such as carbon dioxide retention, it can be used with non-invasive ventilators. Sleep apnea syndrome only requires a single-level ventilator with constant pressure, while lung diseases require a dual-level ventilator with two pressures. According to the judgment conditions of hypoxemia, the family is equipped with an oximeter, and obtaining blood oxygen saturation can quickly understand the physical state of oxygen inhalation.
Key points for purchasing oxygen concentrators
① When the budget is sufficient, you can choose an oxygen concentrator with oxygen concentration monitoring.
② Choose an oxygen concentrator with a large enough compressor exhaust volume. A larger compressor has a relatively longer service life, that is, the machine is larger.
③ If continuous oxygen therapy is required, a good heat dissipation system is required to ensure continuous operation for 24 hours or even 365 days.
④ The greater the compressor power, the higher the noise. Industry standards stipulate that the noise value of the oxygen concentrator should be ≤60dB, and it is more comfortable to reach below 45dB.
⑤ Give priority to oxygen concentrators with functions such as large-screen display and voice prompts to reduce the difficulty of use.
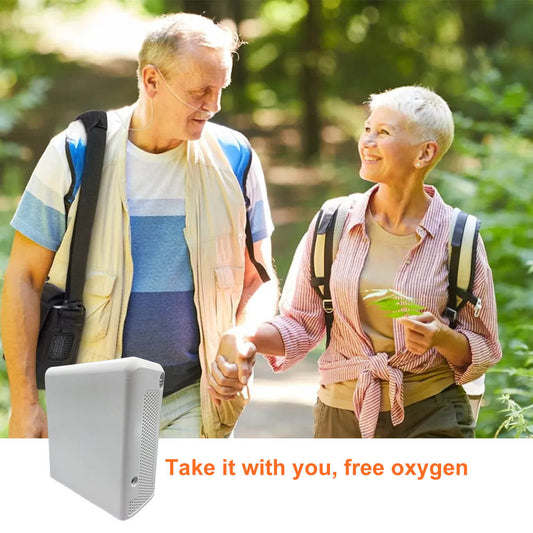
⑥ Patients with unfixed oxygen inhalation positions also need to consider portability.
⑦ Based on your actual needs, choose an oxygen concentrator with a flow rate higher than or equal to the maximum oxygen inhalation flow rate.
⑧ If you need to use it on the plateau, you need to choose an oxygen concentrator with a larger liter.
Clinical parameters of home oxygen concentrators
Hypoxemia judgment
Normal arterial oxygen partial pressure (mmHg) is 102-(0.33×age years). Generally, hypoxemia is defined as arterial oxygen partial pressure below 80 mmHg, and oxygen therapy is required at this time. When blood gas analysis is not performed in the hospital to detect blood oxygen partial pressure, a preliminary judgment can be made based on blood oxygen saturation. If the blood oxygen saturation is below 90%, long-term home oxygen therapy is required, and if it is below 91%-95%, long-term home oxygen therapy is recommended.
Calculation of oxygen therapy parameters
Generally, when using nasal oxygen cannula for oxygen inhalation, it is open oxygen inhalation, and what is actually inhaled is a mixture of the oxygen concentrator output and the surrounding air. If the oxygen concentrator provides X liters of oxygen with a concentration of M (M is between 0 - 1) per minute, the body's inhaled volume is Y (varies from person to person), the oxygen concentration in the air is 0.21, and the inhaled oxygen volume is: X*M+(Y-X)*0.21 = 0.21*Y+(M-0.21)*X, the oxygen concentration is 0.21+(M-0.21)*X/Y, and when 100% oxygen is inhaled, it can be roughly estimated to be 0.21+0.04*X.
Oxygen therapy for various diseases
① Oxygen therapy in the stable stage of chronic obstructive pulmonary emphysema (COPD)
When COPD patients have an arterial oxygen partial pressure of less than 55 mm or an arterial oxygen saturation of less than 88%, or when hypoxemia occurs at night and during exercise, it is recommended to conduct long-term oxygen therapy for more than 15 hours, including sleep time. However, home oxygen therapy is not suitable when the condition is unstable. COPD oxygen therapy advocates low-flow oxygen inhalation, with an oxygen flow rate of 0.5 to 3 liters/minute and an oxygen concentration of <35%, which should be adjusted according to the doctor's instructions.
② Oxygen therapy for cardiovascular diseases
In order to avoid irreversible damage to the heart and brain due to hypoxia, patients with various cardiovascular diseases can effectively avoid complications by supplementing oxygen at the time of onset or just after the onset of the disease.
③ Oxygen therapy for cerebrovascular diseases
Its role in emergency treatment is similar to that of cardiovascular diseases.
The treatment principle of cerebral ischemia is to dilate blood vessels and increase tissue oxygen supply. Those who have the conditions to inhale oxygen can supplement oxygen at an oxygen flow rate of 2 liters/minute until the symptoms are relieved, which accelerates the correction of hypoxia symptoms. The increase in blood oxygen concentration can also reduce blood viscosity and dissolve micro-thrombi. From the second day of onset, oxygen inhalation 1 to 2 times a day, 1 to 2 hours each time, for 2 to 3 consecutive weeks can prevent recurrence.
Cerebral infarction is ischemia and hypoxia of brain tissue in the infarct area. Appropriate oxygen inhalation can increase blood oxygen concentration, reduce blood viscosity and reduce brain tissue damage. For patients with acute cerebral infarction, the oxygen flow rate is mostly 4 liters/minute. During the recovery period, patients can receive oxygen therapy at home, 1 to 2 hours each time, and continuous treatment for two weeks can achieve better recovery effects.
Patients with vertigo can take appropriate oxygen. Increasing blood oxygen partial pressure and blood oxygen content can help alleviate the inner ear hypoxia and gradually relieve symptoms. Oxygen inhalation at home can be once a day, 1 to 2 hours each time, with a flow rate of 1 to 2 liters/minute.
④ Oxygen therapy for diabetes
Oxygen inhalation for diabetic patients can promote aerobic metabolism, increase glucose consumption and lower blood sugar, and increase the production of adenosine triphosphate, etc., which can promote the recovery of pancreatic islet function. The hemoglobin of diabetic patients is highly oxygen-saturated, resulting in a decrease in the amount of physical dissolved oxygen, which causes a certain degree of tissue hypoxia. Oxygen therapy can increase the physical dissolved oxygen. Patients with mild diabetes do not need oxygen therapy if they have no obvious symptoms. Patients with moderate diabetes can generally achieve good results by inhaling oxygen at a flow rate of 4 to 6 liters/minute, once a day, for 2 hours each time, for 3 to 4 weeks. Severe patients should be treated in the hospital according to the doctor's requirements, and the number of oxygen inhalations should be increased.
⑤ Oxygen therapy for cervical spondylosis
Cervical spondylosis with obstruction of vertebral artery blood supply causes brain tissue hypoxia, which can be improved by oxygen inhalation.
⑥ Oxygen therapy for pregnant women and fetal intrauterine distress
Fetal intrauterine distress refers to fetal hypoxia in the mother's body, which can be improved by oxygen inhalation.
⑦ Oxygen therapy for cerebral hemorrhage
Those with conditions can inhale 3-5 liters/minute of oxygen, which can moderately relieve brain hypoxia.
⑧ Oxygen therapy for acute myocardial infarction
Those with conditions can inhale 3-5 liters/minute of oxygen, which can moderately relieve myocardial cell apoptosis caused by hypoxia.
⑨ Oxygen therapy for asthma attacks
Those with conditions can inhale 3 liters/minute of oxygen to relieve hypoxia symptoms.
Note:
Risks and side effects of oxygen therapy: Inappropriate oxygen therapy may cause dryness of the respiratory tract, respiratory depression, oxygen poisoning, etc., so it must be carried out under the guidance of a professional doctor, and the oxygen inhalation time should be reasonably selected, the oxygen flow rate should be controlled, and attention should be paid to the humidification of oxygen to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the treatment.

TOP oxygen concentrator supplier,reliable product and service
DEDAKJ oxygen concentrator manufacturer provides various models of 1-9L home oxygen concentrators, up to 20LPM medical oxygen concentrators as well as the 2 lbs lightweight portable oxygen concentrator for traveling.
This is top-rated DEDAKJ oxygen concentrator supplier, providing both DEDAKJ 10- 20 liter medical oxygen concentrators and 1-9 liters home oxygen breathing machines, and DEDAKJ oxygen accessories parts.
For more information on oxygen concentrators, please feel free to consult us.
And you are we welcome to place the order in our official store directly.
We are operating the USA, Europe, Mexico and UK local warehouses.
Usually you can receive the parcel within 3-6 days,very fast shipping time.
More important, as the honorable oxygen concentrator supplier, we can offer 1 year quality warranty to our customers!