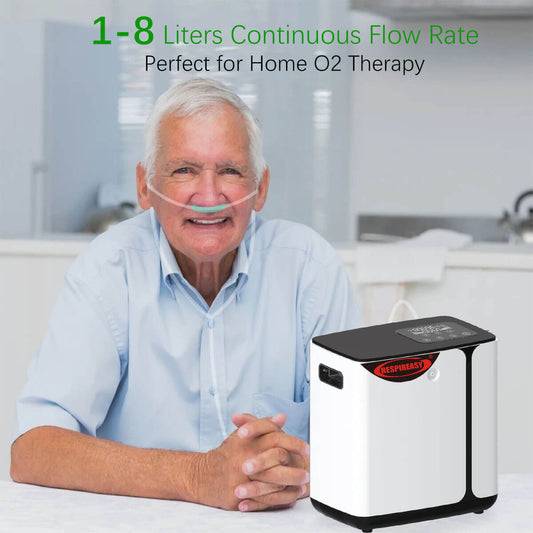
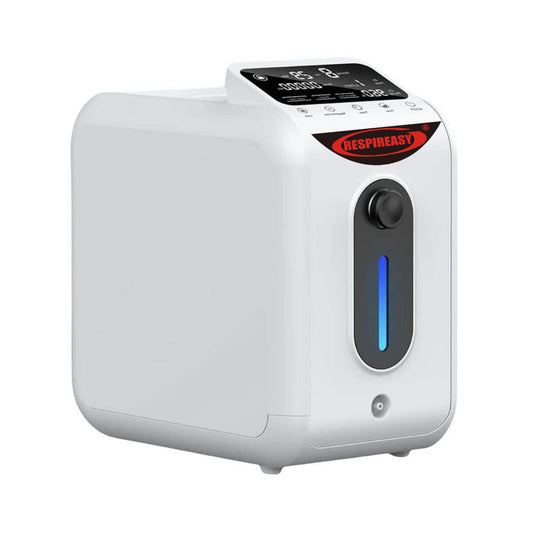
How well do you know about home oxygen concentrators?
Home oxygen concentrators, these compact and practical medical devices, are gradually becoming a must-have for many families. They not only help specific individuals conveniently obtain high-concentration oxygen at home, but are also favored for their simple operation and ease of use. So, how much do you know about home oxygen concentrators?
What is a home oxygen concentrator?
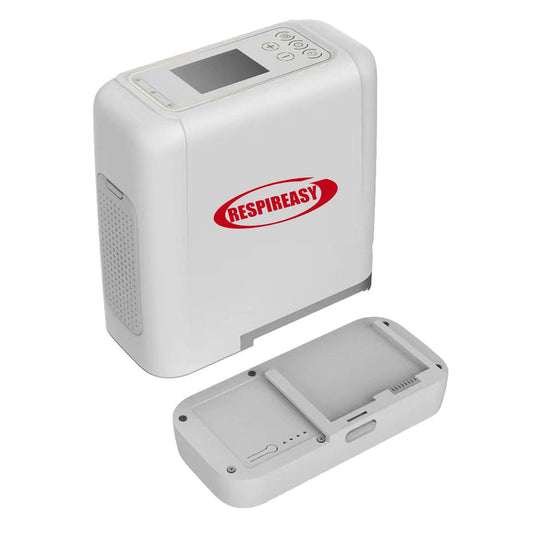
A home oxygen concentrator, also known as a small molecular sieve oxygen concentrator or portable oxygen concentrator, is a device that separates high-purity oxygen (93%±3%) from the air. Its working principle is mainly based on the pressure swing adsorption (PSA) principle, which extracts high-purity oxygen by adsorbing nitrogen and other gases from the air.
Who are home oxygen concentrators suitable for?
Home oxygen concentrators are mainly suitable for patients with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and respiratory system diseases who have hypoxemia, such as patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. These patients can effectively relieve hypoxia symptoms and improve their quality of life by using an oxygen concentrator at home for oxygen therapy. However, for generally healthy families, there is no need to have an oxygen concentrator at home. If you experience symptoms such as chest tightness, shortness of breath, or difficulty breathing, you should seek medical attention promptly.
Working principles and classification of home oxygen concentrators
There are four main working principles for home oxygen concentrators: molecular sieve principle, polymer oxygen-enriched membrane principle, electrolysis of water principle, and chemical reaction oxygen generation principle. Among them, the molecular sieve principle is currently the mainstream working principle for home oxygen concentrators on the market. It utilizes the different adsorption capacities of molecular sieves for oxygen and nitrogen in the air to achieve the separation of oxygen and nitrogen.
Precautions for using home oxygen concentrators
1. Oxygen concentrators cannot be used for emergency rescue. Because it takes some time for the oxygen concentrator to reach a stable oxygen concentration after being turned on, and it cannot work at high flow rates, it is not suitable for emergency situations.
2. Avoid using in humid environments. For molecular sieve oxygen concentrators, the oxygen concentration will decrease if the molecular sieve becomes damp. Therefore, avoid using it in humid environments such as bathrooms and showers, and keep it dry during storage.
3. Pay attention to safe use. The oxygen concentrator should be kept away from fire sources and avoid contact with flammable and explosive materials. During use, the oxygen concentrator should be placed horizontally. Do not tilt, invert, or block the cooling vents of the machine.
4. Pay attention to replacing the oxygen filter regularly. Abnormal noise from the oxygen concentrator, decreased oxygen concentration, and other problems may be caused by an expired or clogged oxygen filter.
How to choose a home oxygen concentrator
When choosing a home oxygen concentrator, you should pay attention to parameters such as flow rate, oxygen concentration, noise level, and power consumption. The flow rate of an oxygen concentrator indicates the amount of oxygen it can output per minute. Common flow rates on the market are 3 liters and 5 liters. You should choose the appropriate model according to your needs. At the same time, patients with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases or neurasthenia are very sensitive to noise, so choosing an oxygen concentrator with low noise is also very important.